- Eine kurze Einführung in die IT-Sicherheit
- IT-Sicherheit für KMU: Neun bewährte Methoden
- Schwachstellenmanagement
- Sicherheitspriorisierung während der Entwicklung
- Datensicherung
- Datenverschlüsselung
- Firewalls
- Einrichtung von Web- und E-Mail-Filtern
- Stärkung der Sicherheitskompetenz des Personals
- Effektive Vorfallreaktionsplanung
- Cybersicherheitskonformität: Gesetzliche Anforderungen und Richtlinien
- Fazit
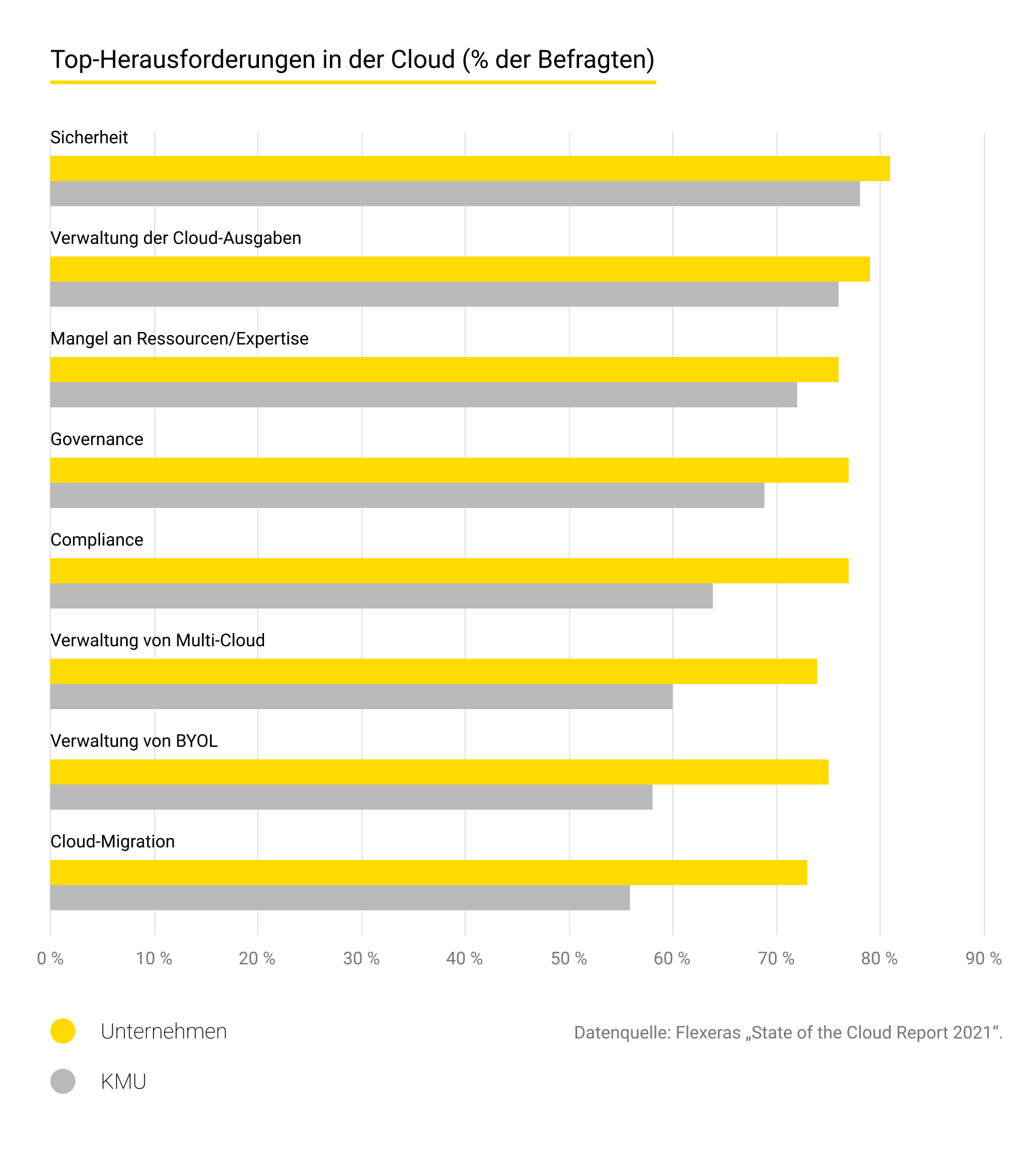
Unabhängig davon, ob ein Unternehmen Cloud-Technologien nutzt (oder Daten in die Cloud migriert) oder nur über eine Website verfügt, sollte die Cybersicherheit einen zentralen Platz in seinem Geschäftsplan einnehmen. Überraschenderweise machen sich jedoch mehr als 60 % der Inhaber von KMU keine Gedanken über dieses Thema. Sie glauben, dass Hacker es nur auf große Organisationen abgesehen haben. Die Fakten sprechen jedoch eine andere Sprache: Laut dem Data Breach Investigations Report von Verizon für 2020 ist jede dritte Datenschutzverletzung mit einem kleinen Unternehmen verbunden.
In diesem Beitrag erläutern Andersens Experten zuverlässige Mechanismen der IT-Sicherheit für KMU, die Firmen implementieren sollten, um unangenehme Situationen zu vermeiden.
Eine kurze Einführung in die IT-Sicherheit
Das Ziel der Cybersicherheit ist es, Computersysteme, Server, digitale Lösungen und die Daten der Endbenutzer vor Angriffen zu schützen, die auf Informationen oder Geld abzielen. Ein zentrales Konzept in der Cybersicherheit ist die Verwundbarkeit, eine Schwachstelle im System oder Netzwerk, die es Angreifern ermöglicht, illegale Aktivitäten durchzuführen, beispielsweise durch Ausnutzung von Fehlern im Programmcode.
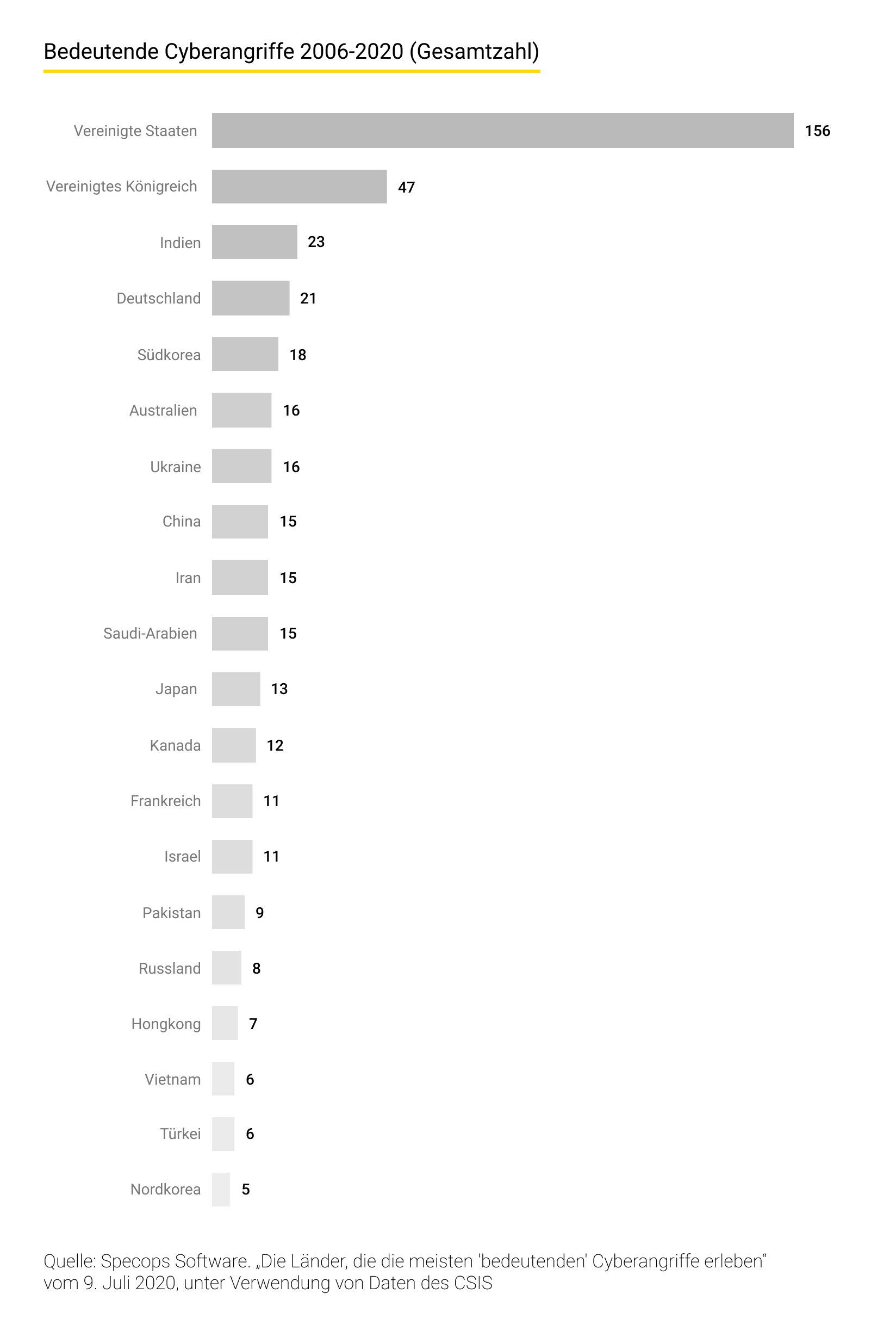
Mit der zunehmenden Digitalisierung greifen Unternehmen vermehrt auf Computer und das Internet der Dinge zurück. Mehr als die Hälfte der Weltbevölkerung ist bereits online, und täglich kommen Tausende neue Benutzer hinzu. In dieser Zeit entwickeln Hacker kontinuierlich neue Methoden, um Daten zu stehlen. Cyberangriffe wurden im Jahr 2021 zu den fünf größten globalen Bedrohungen gezählt.
Angreifer haben heute mehr Gründe als je zuvor, Schwachstellen in Computersystemen auszunutzen: sei es, um Daten zu stehlen, finanzielle Gewinne zu erzielen oder politische Ziele zu verfolgen. Jährlich werden weltweit über 2.000 Datenschutzverletzungen bestätigt, von denen jede im Durchschnitt Kosten in Höhe von 3,9 Millionen US-Dollar verursacht.
Leider suchen Organisationen oft erst dann Unterstützung von Cybersicherheits- und Mediensicherheitsdiensten, wenn bereits ein Vorfall eingetreten ist. Experten betrachten jedoch den Schutz einer Firma als tägliche Priorität, da bereits gelegentliche Transaktionen auf Websites Schwachstellen aufzeigen können. Aufgrund dieser Nachlässigkeit im Umgang mit Cybersicherheit erweisen sich die ergriffenen Maßnahmen häufig als weniger effektiv als möglich.
Paul Lipman, CEO von BullGuard, betont, warum IT-Sicherheit für KMU von entscheidender Bedeutung ist. Er hebt hervor, dass kleine Unternehmen oft zum Ziel von Cyberangriffen werden, da sie wichtige Sicherheitsaspekte vernachlässigen.
Doch bereits ein einziger Angriff kann ausreichen, um „ein Unternehmen in die Knie zu zwingen“. Dieses Risiko kann durch den gezielten Einsatz der folgenden Datenschutzmechanismen vermieden werden.
IT-Sicherheit für KMU: Neun bewährte Methoden
Man sollte effiziente Methoden verwenden, um die IT-Sicherheit für KMU zu implementieren. Andersens Experten haben neun wirksame Praktiken ausgewählt, die Ihnen dabei helfen, Ihre Geschäftsabläufe und sensible Daten zu schützen.
Schwachstellenmanagement
Schwachstellenmanagement ist ein wesentlicher Bestandteil der IT-Sicherheit für KMU. Dabei handelt es sich um eine Strategie, mit der Unternehmen „Lücken“ in ihren Systemen überwachen, beseitigen oder minimieren. Cybersicherheitsspezialisten identifizieren die Art der Schwachstellen und treffen anschließend Entscheidungen darüber, wie sie die Situation beheben und die Organisation schützen können. Es gibt jedoch einige Nuancen zu beachten: Falsche Umsetzungen dieses Prozesses können schwerwiegende Folgen haben.
Die meisten Organisationen verwenden Schwachstellenscanner wie Nessus, Acunetix, Qualys, OpenVAS und andere, die monatlich ausgeführt werden. Diese Programme überprüfen die Infrastruktur, identifizieren Schwachstellen, beheben einige davon und lassen andere ungelöst.
Gleichzeitig stoßen Organisationen oft auf Probleme bei der Bewältigung von Mängeln. Ein häufiges Problem besteht darin, dass neu erstellte virtuelle Maschinen nicht vom Schwachstellenscanner erfasst werden, wodurch sie im Programm unberücksichtigt bleiben. Zusätzlich kann niemand garantieren, dass die virtuelle Maschine fehlerfrei ist, alle erforderlichen Patches enthält usw. Mit dem Wachstum eines Unternehmens wird das Sicherheitsproblem komplexer, und die Identifizierung kritischer Stellen im System wird zunehmend schwieriger.
Selbst bei Verwendung des teuersten Scanners, der von Experten empfohlen wird, deckt seine Schwachstellenbasis oft nicht einmal 85 % aller Fehler ab. Daher werden nicht alle Schwachstellen rechtzeitig erkannt und geschlossen.
Sicherheitspriorisierung während der Entwicklung
Obwohl das Konzept der Sicherheit in der Entwicklung seit etwa 15 Jahren besteht, seit seiner Einführung durch Microsoft, sind sich nicht alle Unternehmen seines Wertes bewusst.
Im agilen Softwareentwicklungsmodell umfasst der Security Development Lifecycle (SDL) Überprüfungen auf Schwachstellen zwischen regulären Sprints sowie eine abschließende Sicherheitsüberprüfung vor der Bereitstellung der Software. In letzter Zeit wird vermehrt über eine neue Methode zur Vermeidung von Schwachstellen gesprochen – DevSecOps –, bei der Sicherheitstests in jede Phase der CI/CD-Pipeline integriert werden.
Trotzdem zeigen sich Geschäftsinhaber, selbst solche, die geschäftskritische Anwendungen für den Finanzdienstleistungssektor entwickeln, nicht besonders eifrig darin, den Security Development Lifecycle oder DevSecOps zu implementieren oder Beratungsdienste für Cybersicherheit in Anspruch zu nehmen. Die meisten von ihnen beschränken sich auf Rezensionen vor der Veröffentlichung.
Warum sind SDL und DevSecOps wichtig? Für Sicherheitstests gilt dieselbe Regel wie für den gesamten Testprozess: Je früher eine Schwachstelle entdeckt wird, desto geringer sind die Kosten für ihre Behebung für ein Unternehmen. Wenn beispielsweise ein Schwachpunkt in der Architektur einer Anwendung erkannt wird, bevor mit dem Codieren begonnen wird, können die Kosten für die Behebung um das Zehnfache geringer ausfallen als bei der Lösung desselben Problems in der Produktionsphase.
Datensicherung
Die Sicherung geschäftskritischer Daten ist unerlässlich, um sie im Falle eines Vorfalls oder Computerproblems wiederherstellen zu können. Spezialisten für IT-Sicherheit bei KMU empfehlen, es zur Gewohnheit werden zu lassen, wichtige Informationen sicher zu speichern, beispielsweise auf einem tragbaren Gerät oder USB, und regelmäßige wöchentliche, vierteljährliche und jährliche Server-Backups durchzuführen.
Die US-amerikanische Small Business Administration empfiehlt, Tabellenkalkulationen, Datenbanken, Finanzdateien und Cloud-Daten zu duplizieren. Auf diese Weise können Unternehmen sich vor den Risiken von Hardware- und Softwareschäden, Viren, Hacks, Stromausfällen und menschlichen Fehlern schützen.
Datenverschlüsselung
Verschlüsselung spielt eine wesentliche Rolle in der IT-Sicherheit für KMU. Dies ist eine wichtige Sicherheitsfunktion, die dazu beiträgt, Benutzer zu authentifizieren und zu autorisieren sowie unbefugten Zugriff auf persönliche Dateien zu verhindern. Laut einer Umfrage von The Manifest gehört Verschlüsselung zu den fünf am häufigsten verwendeten Sicherheitsmaßnahmen, wobei 44 % der Kleinunternehmer dafür stimmten. Die Implementierung dieser Schutzmaßnahme erfordert jedoch sorgfältige Planung und Durchführung.

Geräte enthalten sowohl dynamische Daten (in Bewegung) als auch statische Daten (im Ruhezustand). Dynamische Daten bewegen sich häufig von einem Ort zum anderen, beispielsweise über das Internet, während statische Daten inaktiv sind und auf Festplatten, Computern, Flash-Laufwerken usw. gespeichert sind.
Unternehmer könnten irrtümlicherweise annehmen, dass nur dynamische Daten, die potenziell über das Internet gestohlen werden können, schützenswert sind. Doch in Wahrheit sind statische Daten genauso anfällig und wertvoll für Angreifer. Diese entwickeln ständig raffinierte Methoden, um in Systeme einzudringen und Informationen direkt von Geräten zu entwenden.
In dieser Situation werden sowohl statische als auch dynamische Daten durch Verschlüsselung geschützt und gespeichert. Informationen werden entweder vor dem Senden verschlüsselt oder über gesicherte Verbindungen wie HTTPS, SSL, FTPS usw. übertragen, und zwar auf allen Ebenen des OSI-Modells.
Firewalls
Eine Firewall überwacht die Sicherheit an der Grenze zwischen dem Firmennetzwerk und dem Internet. Sie fungiert als Schutzmauer, die Benutzer vor den negativen Auswirkungen des Internets abschirmt. Dabei arbeitet sie nach einem Satz von Regeln, die festlegen, welcher Datenverkehr erlaubt und welcher blockiert wird.
Deshalb ist die Firewall die erste Verteidigungslinie gegen Cyberangriffe, indem sie eine Barriere zwischen Benutzerdaten und potenziellen Kriminellen errichtet. Obwohl die FCC die Verwendung von Firewalls empfiehlt, hat diese Technologie ihre Schwächen.
Erstens verbringen Administratoren oft viel Zeit damit, die benötigten Informationen zu finden, und sie verstehen nicht immer vollständig, wie sie alle Funktionen nutzen können. Zweitens können Firewalls keine vollständige Transparenz aller Bedrohungen und Risiken bieten. Und drittens ist nicht jeder erfahrene Systemadministrator in der Lage, Firewalls effektiv zu konfigurieren und zu steuern.
Eine präzise Konfiguration und ein klares Verständnis der Firewall-Sicherheit reduzieren Netzwerkrisiken und sind hilfreich für die Festlegung von Architektur, Standards, Richtlinien und Verfahren sowie für das Änderungsmanagement und ähnliche Aspekte.
Einrichtung von Web- und E-Mail-Filtern
Statistiken zeigen, dass etwa 94 % der Malware über E-Mails verbreitet wird. Daher ist der Schutz von Unternehmens-E-Mails durch Filter eine unverzichtbare Maßnahme bei der Implementierung von der IT-Sicherheit für KMU.
Filter sind Regeln, die im Mail-Client oder Mail-Server so konfiguriert werden können, dass sie E-Mails anhand bestimmter Kriterien automatisch herausfiltern. Auf diese Weise können Mitarbeiter vor Spam- und Phishing-Bedrohungen geschützt werden. Die Einrichtung von Webfiltern beinhaltet die Implementierung von Blacklist-Diensten, die Benutzern den Zugriff auf verdächtige Websites verweigern. Ein unbeabsichtigter Besuch einer gefährlichen Ressource durch einen unaufmerksamen Mitarbeiter kann ausreichen, um das Unternehmenssystem mit Malware zu infizieren.
Stärkung der Sicherheitskompetenz des Personals
Die Einführung fortschrittlicher Sicherheitslösungen ist wirkungslos, wenn den Mitarbeitern das Verständnis für die grundlegenden Prinzipien der IT-Sicherheit für KMU fehlt. Experten schätzen, dass bis zu 90 % der Datenschutzverletzungen auf menschliche Fehler zurückzuführen sind. Dies kann auf Phishing-Betrug, die Verwendung schwacher Passwörter oder den unangemessenen Umgang mit sensiblen Daten zurückzuführen sein. Kein System ist vor menschlichen Fehlern immun.
Deshalb ist eine fortlaufende Schulung in Cybersicherheit für alle Mitarbeiter unerlässlich. Die Bildungsmaßnahmen sollten über eine einmalige Orientierung hinausgehen und dazu beitragen, eine Organisationskultur der Sicherheitsbewusstheit aufzubauen. Eine effektive Schulung sollte die folgenden Aspekte abdecken:
- Sichere Passwortrichtlinien: Anleitung zur Erstellung von Passwörtern mit angemessener Länge, Komplexität und Verwaltung von Anmeldeinformationen. Nutzen Sie Passwort-Manager zur Unterstützung;
- Phishing-Erkennung: Durchführen von simulierten Phishing-Angriffen. Schulen Sie Ihre Mitarbeiter darin, Warnsignale in E-Mails zu erkennen, wie verdächtige Links oder Anhänge;
- Sichere Internetnutzung: Seien Sie vorsichtig beim Zugriff auf illegale oder fragwürdige Websites, die Malware verbreiten können;
- Social-Engineering-Risiken: Aufklärung über Täuschungsmethoden, bei denen versucht wird, Mitarbeiter zur Preisgabe von Daten zu manipulieren;
- Datenverarbeitung: Verschlüsselung von Geräten, sichere Dateifreigabe, Vermeidung der Nutzung öffentlicher WLAN-Netzwerke für vertrauliche Informationen;
- Meldung von Vorfällen: Klare Anweisungen zum Melden potenzieller Verstöße an die IT/das Management;
- Risiken im Homeoffice: Mit der zunehmenden Fernarbeit müssen Mitarbeiter auch ihre Heimnetzwerke und Geräte schützen;
- Einhaltung von Vorschriften: Schulung zur Einhaltung von Datenschutzbestimmungen und -richtlinien.
Fortlaufende Sicherheitsworkshops, Vorträge, Analyse von Fallstudien und Quiz fördern das Lernen. Durch Gamification, wie zum Beispiel Cybersicherheitswettbewerbe, wird das Training interaktiv und wettbewerbsorientiert gestaltet.
Letztendlich sollte jedes Teammitglied IT-Sicherheit für KMU als integralen Bestandteil seiner Rolle betrachten. Der Aufbau einer kompetenten Belegschaft ist ebenso wichtig wie die Nutzung der neuesten IT-Lösungen. Gut ausgebildete Mitarbeiter, die in der Lage sind, Bedrohungen zu erkennen und abzuwehren, stellen die beste Verteidigung eines Unternehmens dar.
Effektive Vorfallreaktionsplanung
Obwohl proaktive Maßnahmen zur IT-Sicherheit für KMU von entscheidender Bedeutung sind, ist es ebenso wichtig, über einen effektiven Plan zur Reaktion auf laufende Angriffe zu verfügen. Ein Vorfallreaktionsplan umfasst festgelegte Rollen, Verantwortlichkeiten und detaillierte Verfahren für den Fall eines Verstoßes. Dieser Plan für schnelles Handeln ist notwendig, da die ersten Stunden und Tage nach einem Angriff entscheidend für die Schadensbegrenzung sind.
Experten des Ponemon Institute haben herausgefunden, dass die Gesamtkosten einer Datenschutzverletzung um bis zu 14 US-Dollar pro Datensatz gesenkt werden können, wenn ein Reaktionsplan schnell und effektiv umgesetzt wird. Ein gut ausgearbeiteter Plan stellt sicher, dass alle Beteiligten wissen, wie sie einen Vorfall erkennen, kommunizieren, bewerten und darauf reagieren können. Die Vorbereitung dieser Reaktionsverfahren im Voraus ermöglicht es Organisationen, Verwirrung zu vermeiden und Verzögerungen zu minimieren.
Ein angemessener Plan sollte Maßnahmen zur Vorbereitung, Identifizierung, Analyse, Eindämmung, Beseitigung und Wiederherstellung nach einem Verstoß umfassen. Außerdem sollten darin Erkenntnisse aus einem Vorfall festgehalten werden.
Der Plan sollte den Mitgliedern des Incident-Response-Teams Rollen entsprechend ihrer Fähigkeiten zuweisen. Zum Beispiel können sich Systemadministratoren auf die technische Eindämmung konzentrieren, während sich die Rechtsberatung um Compliance-Fragen kümmert. Leitende Angestellte treffen strategische Entscheidungen, während PR-Spezialisten für die öffentliche Kommunikation zuständig sind.
Es ist ebenfalls wichtig, den Vorfallreaktionsplan regelmäßig durch simulierte Angriffe zu testen. Diese Übungen bereiten das Team darauf vor, die Abläufe auch in stressigen Situationen einzuhalten. Sie helfen dabei, potenzielle Lücken, Ineffizienzen oder Unklarheiten im Plan zu identifizieren, bevor es tatsächlich zu einem Sicherheitsvorfall kommt. Durch das Üben und Optimieren des Reaktionsplans wird die Bereitschaft gestärkt und die Reaktionszeit verkürzt, wenn ein Vorfall eintritt.
Gemäß einer Studie von IBM können Unternehmen durch die Einführung eines Plans zur Reaktion auf Cyber-Vorfälle 2,66 Millionen US-Dollar einsparen.

Cybersicherheitskonformität: Gesetzliche Anforderungen und Richtlinien
Mit dem zunehmenden Auftreten von Cyberangriffen setzen staatliche Vorschriften Firmen unter Druck, Sicherheitsvorkehrungen ernsthafter zu nehmen. Die Nichtbefolgung verbindlicher Datenschutzgesetze kann zu erheblichen Geldstrafen und Reputationsverlusten führen. Zu den wichtigsten Normen für die Einhaltung der Cybersicherheit gehören:
- PCI DSS: Dieser Standard gilt für alle Organisationen, die Kreditkartendaten verarbeiten, speichern oder übertragen. Zu den erforderlichen Schutzmaßnahmen gehören Zugriffskontrollen, Verschlüsselung, Schwachstellenmanagement und mehr. Bei Nichtbeachtung können Geldstrafen zwischen 5.000 und 100.000 US-Dollar pro Monat verhängt werden.
- HIPAA: Der Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act regelt den Schutz von Gesundheitsdaten. Er legt technische, physische und administrative Kontrollen für Gesundheitseinrichtungen und ihre Geschäftspartner fest. Die Strafen für Verstöße können bis zu 1,5 Millionen US-Dollar pro Jahr betragen.
- DSGVO: Die Datenschutz-Grundverordnung der Europäischen Union stellt strenge Datenschutz- und Sicherheitsvorschriften für personenbezogene Daten von EU-Bürgern auf. Die Bußgelder gemäß der DSGVO können entweder 4 % des weltweiten Jahresumsatzes oder 20 Millionen Euro betragen, je nachdem, welcher Wert höher ist.
Um Sanktionen von Behörden zu vermeiden, sollten Firmen umfassende Cybersicherheitsrichtlinien, Kontrollen und Mitarbeiterschulungen einführen, um die vollständige Compliance zu gewährleisten. Regelmäßige Audits und Risikobewertungen helfen dabei, Lücken zu identifizieren und zu beheben. Kluge Investitionen in die Compliance können langfristig wesentlich höhere Kosten verhindern.
Fazit
IT-Sicherheit für KMU ist für die Kundenbindung und somit für den Geschäftserfolg einer Firma von entscheidender Bedeutung. Das Vertrauen der Verbraucher in eine Marke beeinflusst unmittelbar die Umsätze. Zudem nehmen die rechtlichen Vorschriften zu, die vertrauliche Informationen von Kunden und Mitarbeitern schützen, und deren Nichtbeachtung kann zu Strafen führen. Angesichts der zunehmenden Anzahl von Cyberangriffen müssen KMU sicherstellen, dass ihre Sicherheitsmaßnahmen funktionsfähig sind und in der Lage, alle Arten von Bedrohungen abzuwehren.
Wenn Sie keinen erfahrenen Systemadministrator in Ihrer Organisation haben, ist es ratsam, Dienstleistungen zur IT-Sicherheit für Unternehmen in Betracht zu ziehen. Ein externer Experte analysiert Ihre bestehende Infrastruktur, bewertet objektiv Ihr Sicherheitssystem und empfiehlt die besten Maßnahmen zur Verbesserung desselben. Dabei entwickelt er Richtlinien für das Schwachstellenmanagement, entwirft Schulungsprogramme für Mitarbeiter und erstellt eine Strategie zur Stärkung der Cybersicherheit. Durch die Bewertung von Bedrohungsrisiken, die Implementierung von Änderungen und die Förderung einer Sicherheitskultur können Sie Ihr Unternehmen effektiv schützen.






