- What the main features of a discovery phase are
- What product discovery techniques do our skilled Business Analysts use?
- Design thinking
- Empathize
- Define
- Ideate
- Prototype
- Test
- Conducting interviews
- Brainstorming
- Business modeling
- Functional decomposition
- Conclusion
Thousands of software development projects are started all over the world every year. They differ a lot in terms of workload and budgets. Some of them can be accomplished by several software developers in just a few weeks, while others require thousands of working days. From the perspective of a non-professional, these projects are very hard to estimate. For example, when comparing Amazon with a small online store, to a layperson they can look almost the same. However, the difference in their workload is dramatic. Improper estimations are one of the reasons why, according to McKinsey, 45% of software development projects run over budget, sometimes even by several times. To avoid problems, Andersen's experts strongly recommend that our customers start each project with a discovery phase. Read on to learn what effective product discovery techniques we offer our customers to ensure in-depth analysis of their business ideas.
What the main features of a discovery phase are
In short, a discovery phase leads to the following results:
- understanding your users’ needs;
- understanding the context of your project and product from a market, business, and technological perspective;
- creating an exhaustive and closed list of features and defining the project scope;
- developing and testing prototypes;
- making key architectural decisions;
- making estimations, prioritizing features, and planning the development.
The discovery phase of a project is characterized by the highest possible uncertainty. It requires creativity and well-established communication between Business Analysts and the customer. In addition, it has tight deadlines. Therefore, conducting a successful discovery phase requires using appropriate techniques.
What product discovery techniques do our skilled Business Analysts use?
Design thinking
Design thinking is an old concept formulated in its current state in the 1990s by David Kelley and Tim Brown. It’s not only a philosophy but also a process that consists of five iterative steps.
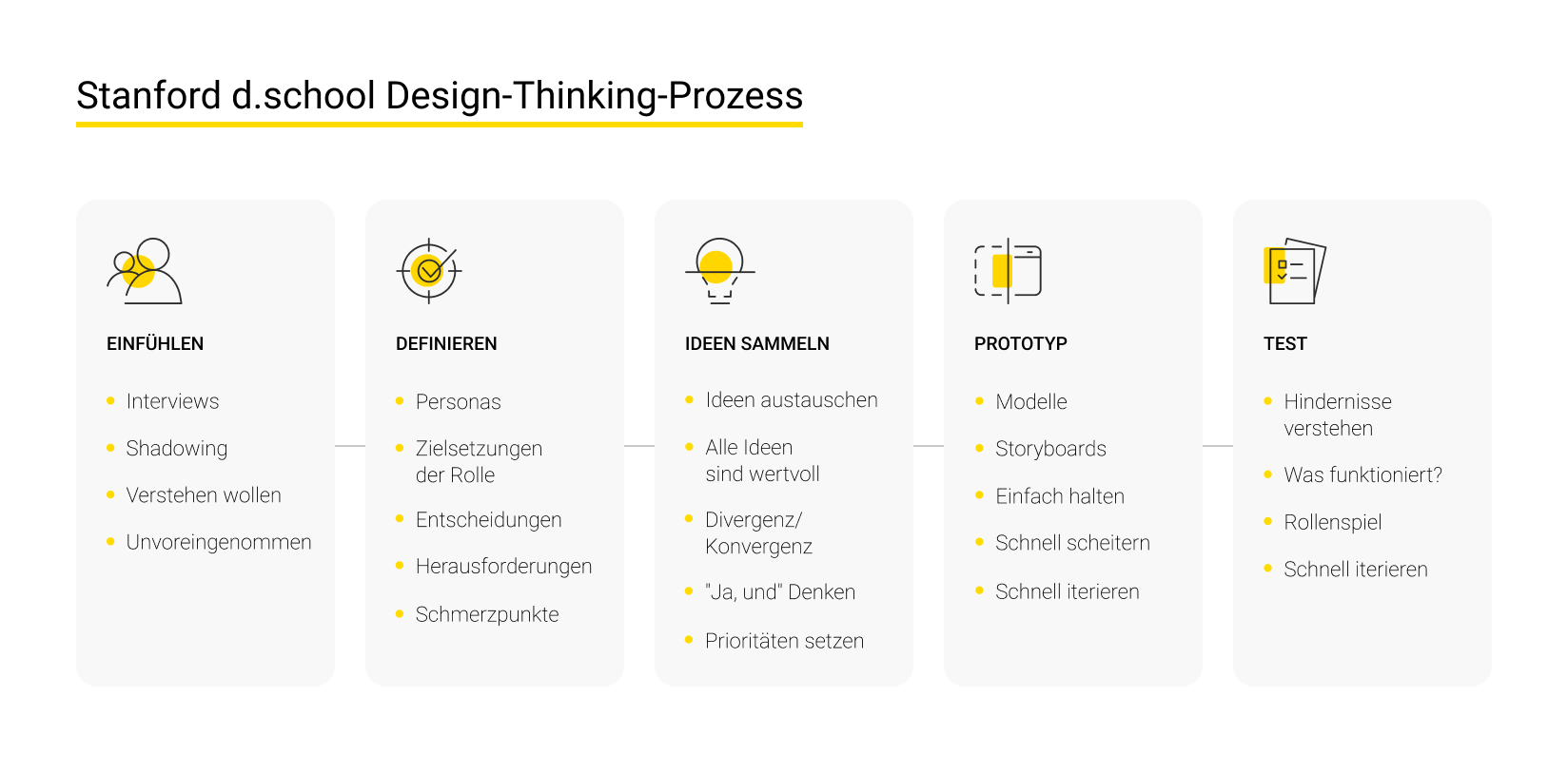
Empathize
In this step, Business Analysts formulate assumptions about the pain points of the potential users:
- What problems are they experiencing?
- How do they currently solve them?
- Are these problems really important?
- Are people ready to pay for solutions?
The specialists shouldn’t convince the customer of anything; their goal is to understand the users.
Define
Organizing and analyzing data collected in the previous step helps the experts to articulate the main problems that the software will solve, the so-called problem statements, and create personas.
Ideate
This step refers to brainstorming as many ideas related to software features that will solve the problems as possible. None of the ideas are wrong at this stage, excluding those that are impossible to implement.
Prototype
The less time it takes to create prototypes of possible solutions, the better. These prototypes can take the form of sketches on a napkin or PowerPoint presentations. They should be minimalistic and just enough to make the potential users understand the idea of how the software is going to work.
Test
Asking potential users for their opinion about the prototypes can include the following questions:
- Does the software solve the problem?
- Is it convenient to use?
- Is it priced properly?
The process of improving and testing the prototypes should be iterated until the solution can solve potential users' relevant problems in an appropriate and convenient manner.
Conducting interviews
When providing product development services, interviewing is essential to collect relevant and useful data about a project. An open conversation with potential customers makes them feel confident and provides the project team with more insights.
A good interview shouldn’t take more than twenty minutes and shouldn’t include overly intrusive questions. Interviewers are often tempted to ask about the respondent’s annual revenue and similar topics. However, there is little possibility that they will answer openly as this would involve proprietary information that the respondent might not be willing to disclose. Moreover, they can get irritated by such questions. Instead of inquiring about the prospective customer’s annual revenue, it’s appropriate to ask them about prices for their services and products.
Both using a standard questionnaire and asking clarifying questions are essential. When conducting product discovery, one needs insights and not statistics. Asking open-ended questions provides Business Analysts with the necessary information and helps the respondents to remain engaged during the interview.
Brainstorming
The goal of brainstorming is to find non-standard and effective solutions to problems. During brainstorming, its participants propose the solutions that first come into their minds no matter how strange they might seem. The majority of the proposals are later discarded; however, discussing as many ideas as possible is essential to turn quantity into quality. The main idea behind this process is to articulate the best ideas by employing creativity and full freedom while generating them.
Brainstorming brings the following results:
- proposing original solutions to users’ problems;
- eliciting as many possible product features as possible so as not to miss anything important;
- revealing possible product limitations, for example, dictated by the company policy.
Business modeling
Different projects require different business modeling techniques. For example, working on a business model for a startup usually involves using Lean Canvas.

When the product is a large corporate system, it requires establishing business processes.
No matter what type of business modeling is required on a project, it’s always better to involve experienced Business Analysts who will promptly create consistent, holistic, and usable models.
Functional decomposition
This may seem an easy task, however, many project teams experience difficulties with estimations due to incorrect approaches to creating a work breakdown structure. Specialists who perform decomposition should be skilled in business analysis as they need to understand how the product will work. Otherwise, tasks can be duplicated or unclear from the technical point of view, and therefore, hard to estimate. The lack of qualification in business analysis can lead to missing critical requirements which results in the underestimation of a project, sometimes by several times.
Conclusion
The above techniques are most frequently used during product discovery. Andersen’s teams employ efficient product discovery technique tools in the initial stages of software development projects so that they can be completed on time and within budget. Should you have any questions when planning a project, feel free to contact us, and our top-notch Business Analysts will be happy to provide you with accurate estimations.